
The following map highlights the state-by-state economic impact (in millions of dollars $) across the country. The major concentrations in California, Texas, Florida, Virginia/Maryland, Colorado, Ohio, and Alabama are obvious. New York is home to one of the largest state “NASA economies” outside of the “Big 8”.
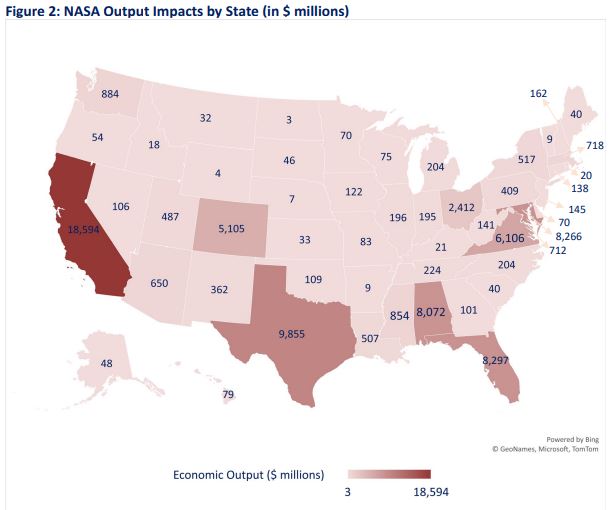
Source: NASA report pg. vi
Empire Space has previously documented the size, scope, and depth of New York’s slice of this NASA economy. This report will highlight the changes between the FY2021 and FY2023 reports, as well as detail some of the specific areas of New York’s space economy that benefit from ties to NASA.
The reality remains that New York is a major player when it comes to the economic impact and job creation benefits that come from doing business with America’s space agency. NASA’s measured direct and indirect employment impacts total almost 2,000 New Yorkers with an economic impact over $500 million annually that generates almost $28 million in tax revenues for the State of New York.
Before digging into the numbers, the broad basis for NASA’s economic impact analysis is threefold:
“The impact estimates reported in this study are the sum of three channels of economic impact: (1) the direct contribution of NASA’s own activities; (2) indirect (procurement) activities within NASA’s U.S. supply chain; and (3) the induced effect that results as federal civil servants at NASA facilities, employees of contractors, and employees within the supply chain of those contractors spend their wages in the wider consumer economy,” (NASA).
The following sections will detail how these numbers break down for New York and how they relate to other states across the country.
Job Totals Dip Amid Nationwide Slump
In FY2021, New York was credited with 2,321 jobs supported by direct contracts with NASA, good for 15th largest NASA-affiliated workforce in the US. Additional research by Empire Space has identified roughly 29,000 jobs supported by NASA-related work, utilizing a broader definition of NASA affiliation that includes the full number of employees working at a given company.
The FY2023 NASA report indicates that the 2,321 figure has dipped to 1,975 or 17th largest in the nation. This amounts to a decline of 346 or -14.91%, which was the 32nd worst growth rate in the nation and more significant than the overall -9.73% contraction nationwide.
This detailed NASA chart shows breakdowns by type of impact across both the employment and procurement dimensions.
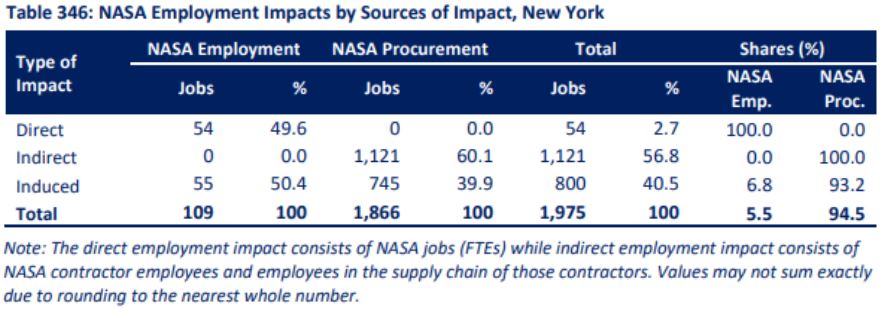
Source: NASA report pg. 264
Unfortunately NASA does not break this number down by specific firms, so it is not possible to reference this data to the itemized database maintained by Empire Space. New York was not an outlier, with 33 of 51 states recording some measure of job decline in the last two years. This indicates a more general contraction of NASA’s employment footprint nationwide, which would make sense given a tighter federal budget environment that has predominated in recent years.
This decline could indicate an actual real-world loss of jobs or simply indicate that NASA contracted less work with New York based firms in FY2023 than FY2021. Under either scenario it is still critically important for NASA connected firms in New York to diversify their portfolio to include non-NASA clients to ensure viability if and when NASA contract work declines.
New York state government also plays a role in supporting these NASA related firms during a downturn such as this. Providing growth incentives and programming resources can fill gaps companies face when their NASA related work declines while encouraging diversification and development that can ensure market share.
Empire Space will continue to track this trend over time and measure New York’s performance against peer states and the nation as a whole. Empire Space is also working to develop annual in-state business surveys that will allow for more precise tracking of job gains and losses within the space sector.
Regardless of the cause, New York should be growing the number of NASA related jobs in the state, not losing them. Much work remains to ensure this number is growing, not shrinking, in the years ahead.
Economic Activity Slips But Nationwide Ranking Rises
In FY2021, NASA documented $531 million in economic activity, which ranked 15th nationally. However this figure had declined by 2023, as was the case with many states during the same time period.
In order to conduct a proper relative analysis of changes in FY2023 it was necessary to adjust for inflation, using a cumulative rate over this 2 year time period of 12.4%. This means $1 in 2021 would be worth $1.12 in 2023. Regarding the economic impact of NASA related work in New York, this increases the FY2021 number to $594.72 million.
NASA’s documented economic impact in New York for FY2023 had declined to $517.34 million, an absolute decrease of just over $77 million and a decline of -13.01%, which was the 35th worst growth rate in the nation over that time period.
The following chart breaks down the “output impact” (economic activity generated) by NASA in both the employment and procurement dimensions.

Source: NASA report pg. 265.
New York was not alone during this time period, with 29 states registering economic impact contractions and only 22 recording gains. The average contraction in states that shrank was 21.46%, meaning there were numerous states that saw a far greater drop off in economic impact.
Many of the states with the highest or lowest growth rates were small states that had small NASA footprints in 2021, such as North Dakota (-59%) , Alaska (-53%), Delaware (+150%), and Maine (+88%), all of which are among the 15 smallest states with a NASA footprint. New York was clustered in the middle of the pack with generally larger states of roughly equal size, which helps put these declining figures in an appropriate context. Ohio is 8th on overall size list in 2023 and declined -12.47%, Arizona is right next to New York at 13th overall and declined at -18.39%. And Louisiana on the other side at 15th declined -8.3%,
Despite declining in absolute size, New York’s NASA economic footprint actually nudged up a rank nationwide, winding up at 14th in 2023 compared to 15th in 2021. This is due to the precipitous drop that occurred in Utah over those two years, where a roughly $600 million (-55%) economic impact contraction dropped the Beehive State from 10th to 16th.

This data likely indicates that the decline in NASA’s economic impact in New York is not due to unique factors in the state, but part of broader nationwide dynamics that mirror similar contractions in NASA’s workforce impacts highlighted in the previous section. New York performed similarly to other peer states in the same timeframe, and even saw our nationwide ranking increase a slot.
A decline is still a decline though, and this data draws attention to the need for New York to increase support for NASA-affiliated businesses to spur new economic growth and activity across the state. Empire Space will continue tracking these figures and conducting additional analysis to understand the deeper dynamics at play behind this decline.
Variable Moon-to-Mars Program Data Impacts Assessment
NASA also provides specific data for the jobs and economic impact from the Moon-to-Mars program, the space agency's plan to return humans to the Moon as a step on the road to Mars. Empire Space analyzed the Moon-to-Mars program for the 2021 data, and NASA provided this data for 2023, yet there is very significant variation between the two years from state to state, to the point where Empire Space hesitates to provide concrete trend analysis on a nationwide scale.
This is likely due to the highly fluid and localized nature of the Moon-to-Mars program, with a smaller number of contracts in more targeted areas of the space sector playing an outsized role in the dataset. Another reality is that Moon-to-Mars related projects are very concentrated in a handful of major states, with most states experiencing small but highly variable year to year changes in impacts. This all makes nationwide trend comparisons very difficult.
The NASA data for Moon-to-Mars impacts in New York does align with the broader economic data, indicating a decline that appears to be roughly on par with peer states.
In 2023 NASA attributed 151 New York jobs to the Moon-to-Mars program. In 2021, NASA attributed 198 jobs in New York to work related to the Moon-t0-Mars program. indicating a decline of over 23% in the last two years. This amounts to a nationwide ranking decline from 15th to 19th. In 2023 NASA attributed a $40.8 million economic impact to the Moon-to-Mars program, a decline of 30.2% from an (inflation adjusted) $58.47 million in 2021. These totals are roughly 8% of NASA's total employment and economic impacts in New York.
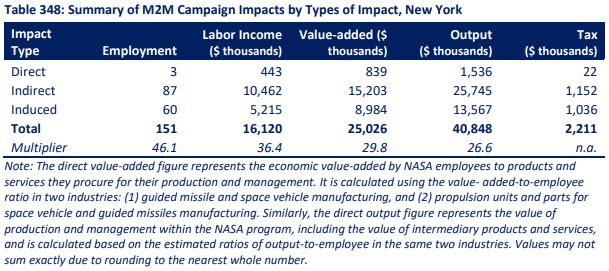
Source: NASA report pg. 265.
This decline largely mirrors the broader declines New York experienced in NASA related jobs and economic activity from Fy2021 to FY 2023, so this data is not unexpected.
Companies that participate in the Moon-to-Mars program are typically highly specialized. New York can reinforce its share of this market by supporting the unique space sector companies that contribute to this vital exploration pipeline.
Diverse NASA Connections Remain Across New York’s Economy
Empire Space has regularly documented New York’s many connections to NASA and its entire exploration portfolio.
A January 2024 analysis of all New York firms with any relationship past or present to any NASA program identified 84 companies with a total statewide employment over 20,000. NASA’s Artemis program specifically is currently or previously affiliated with at least 64 New York based companies that collectively employ more than 18,000.

As the map indicates, these companies are both large and small and exist in every corner of the state while offering a range of unique specializations and skills that fit into NASA’s supply chain.
The reason the Empire Space employment figures are much larger than the NASA employment figures is because Empire Space counts the entire workforce of a relevant firm with any NASA connection towards the overall total, and also includes firms that have done work for NASA in the past, even if they are not doing so currently. NASA’s figures are more narrowly tied to the direct and indirect impacts of existing NASA employment centers or NASA procurement contracts.
NASA also operates the Goddard Institute for Space Studies (GISS) at Columbia University in Manhattan. GISS is a key atmospheric and climate research center, and “interdisciplinary initiative addressing natural and man-made changes in our environment that occur on various time scales — from one-time forcings such as volcanic explosions, to seasonal and annual effects such as El Niño, and on up to the millennia of ice ages — and that affect the habitability of our planet,” (NASA GISS).

Armstrong Hall at Columbia University, home to NASA’s Goddard Institute for Space Studies. (Image source: NASA).
NASA’s climate portfolio generates a range of employment and economic activity impacts across the state. Direct and indirect employment is estimated at 474 jobs, with an total economic impact output of $124 million, generating over $6.5 million in annual tax revenue. These figures are roughly 24% of NASA's total employment and economic impacts across the state.
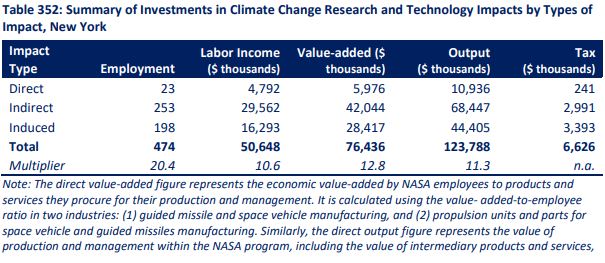
Source: NASA report pg. 267.
There is also an active statewide network of NASA Solar System Ambassadors that conduct space and STEM related community programming. These Ambassadors are a vital resource that connects the general public to space exploration and can serve as key networking agents between different sectors of the space ecosystem within their communities.
These NASA connections offer a tremendous economic opportunity for New York in the future. They provide a foundation of thousands of jobs and hundreds of millions in economic activity generating millions of dollars of tax revenue while enriching our communities.
Future Steps and Action Items
Empire Space will continue to refine this analysis, and will conduct annual reviews with the latest data available from NASA. Please contact info@empirespace.org with any questions, comments, or suggestions.
Private companies in the New York space ecosystem with NASA connections should make sure to take advantage of various state-level programs that can support their operations.
New York state-level economic and government leaders should deepen their awareness of these NASA affiliated employers and work to strengthen this network moving forward. Targeted economic incentives and investments can reinforce these companies when NASA business declines and help them innovate to achieve larger market share in future years.
While the numbers from 2021 to 2023 show some declines in New York’s NASA related workforce and economic impact, the foundation remains for future growth and the Empire State remains a Top 20 space ecosystem powerhouse in the American space economy.